Streaming subway data to a Data Grid in Views
Beta - For evaluation and trial use only
Streaming to Views is currently in beta.
- Refer here to the standard terms related to beta features.
- We invite you to use this beta feature and to provide feedback using the portal available here.
- Refer here for known limitations of this beta feature
The purpose of this walkthrough is to showcase the ability of kdb Insights Enterprise to visualize streaming data in real-time in a View, by streaming the latest co-ordinates of a set of NY City subway trains to a data grid.
We have provided a Kafka subway feed for use in this walkthrough. This feed generates live alerts for NYC subway trains, tracking which trains are stopped at stations. For each train it provides arrival time, station location coordinates, direction and route details.
In this walkthrough you will:
- Create a pipeline to ingest and transform the subway data
- Create a View with a Data Grid to display the data
Create a pipeline
Begin by opening the Pipeline editor by clicking [+] on the ribbon menu and clicking Pipeline, as shown below, or by clicking [+] beside Pipelines on the left-hand menu.
The pipeline editor opens, as shown below.
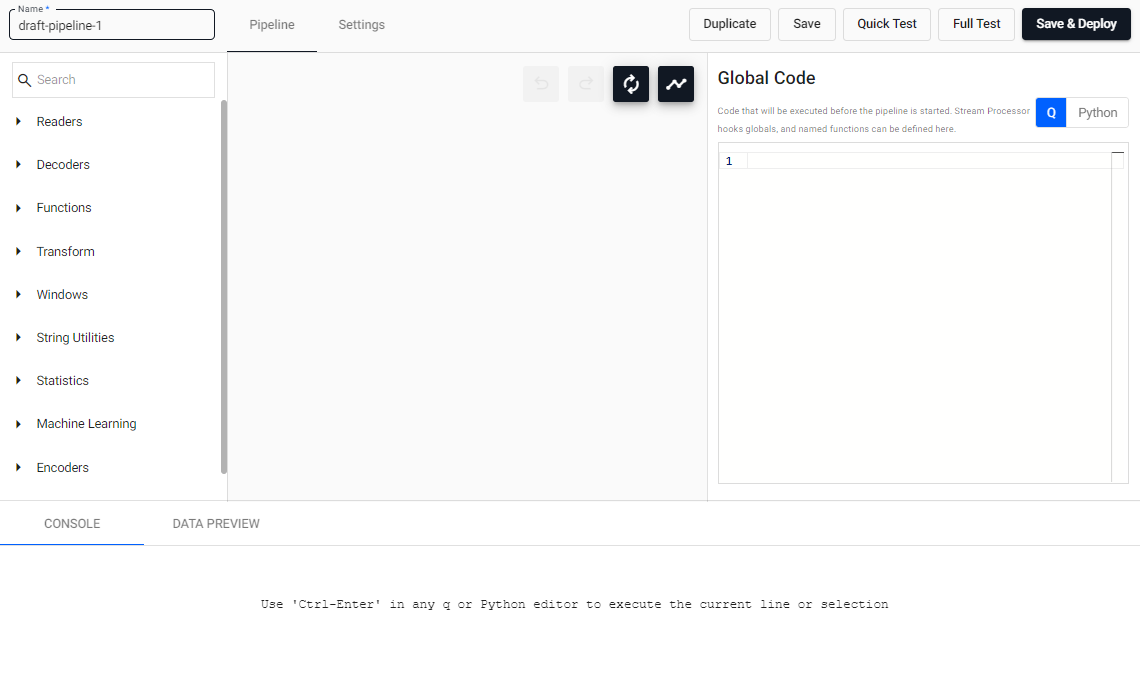
The pipeline requires the following:
- Kafka Node to ingest the data
- Decoder Node to decode the data
- Map Node to convert the decoded data to a kdb+ table
- Transform Node to convert data fields to kdb+ compatible types
- Subscriber Node to provide real-time updates of data
- Environment Variable to ensure the subscriber node updates the stream every 10th of a second
Once these are configured you can save and deploy the pipeline. You can then:
Add a Kafka node
You begin your pipeline with a Kafka node to read the data from the subway feed we have provided.
-
Click-and-drag a Kafka node, from the Readers, into the workspace.
-
Select the Kafka node and add the following connection details to the Configure Kafka Node panel:
setting value Broker kafka.trykdb.kx.com:443 Topic subway Offset End Use TLS Unchecked Use Schema Registry Unchecked -
Expand the Advanced parameters section and tick Use Advanced Kafka Options. Click the [+] to add an advanced configuration and enter the following key value pairs:
key value sasl.username demo sasl.password demo sasl.mechanism SCRAM-SHA-512 security.protocol SASL_SSL -
Click Apply to apply these changes to the Kafka node.
Add a Decoder node
Kafka event data is in JSON and has to be decoded to a kdb+ friendly format (a kdb+ dictionary).
-
Click-and-drag a JSON decoder node, from the Decoders, into the workspace, and connect it to the Reader node.
-
Keep the default JSON decoder settings.
Add a Map node
The decoded data needs to be converted to a kdb+ table. The Map node converts an incoming dictionary to a table using an enlist.
-
Click-and-drag a Map node, from the Functions, into the workspace, and connect it to the Decoder node.
-
Select the Map node and replace the code in the right-hand Configure Map Node property panel with the following code:
{[data] enlist data } -
Click Apply to apply these changes to the Map node.
Add a Transform Node
The next step is to add a Transform node which transforms the subway data fields to kdb+ compatible types and drops the fields that are not going to be displayed in the View.
Converting strings to symbols for use as keyed columns in the Subscriber node
The data from Kafka that is used in this example includes strings. The Subscriber node requires any columns defined as keyed columns to be symbols. This step is required to convert the strings to symbols.
If you are using a Subscriber node with your own data and the data in your keyed columns are already symbols this step is not necessary. See the next section for details on keyed columns.
-
Click-and-drag the Apply Schema node from the list of Transform nodes and connect it to the Decoder node.
-
In the Schema section click the [+] icon under the "add schema columns below" text. Then add the following columns, leaving Parse Strings set to
Autofor all columns:column name colomn type arrival_time Timestamp stop_name Symbol stop_lat Float stop_lon Float direction_id Symbol route_long_name Symbol route_color Symbol -
Click Apply to apply changes to the node.
Add a Subscriber node
A Subscriber node emits a summarized view of the input data, with one record per unique combination of values in the list of keyed columns. The remaining columns are set to their latest values.
Once deployed, the emitted stream of data is available as a data source in a View. This is described in the Create a View section later.
In this example the node is configured so that it emits updates to the co-ordinates of trains per route and direction of travel (i.e. inbound or outbound).
-
Click-and-drag the Subscriber node, from the list of Writers into the central workspace, and connect it to the Apply Schema node.
-
Select the Subscriber node and set the Table to
subway. -
Add the following Keyed Column values:
value route_long_name direction_id Defining these keyed columns ensures that:
-
The output of the Subscriber node has one record per train route and direction.
-
You can filter these columns in the View, as you can only filter on Keyed Columns.
-
-
Click Apply to apply these settings.
Configure the pipeline settings
An environment variable needs to be added to the pipeline to ensures the subscriber node updates the stream every 10th of a second.
-
Click on the Settings tab for the pipeline.
-
Scroll down to the Environment Variables and click Add Variable. Add the following variable details.
variable value details KXI_SP_SUBSCRIBER_PUBLISH_INTERVAL 100 This determines how regularly the subscriber updates the web-socket
Save and deploy the pipeline
The pipeline is now configured and ready to be saved and deployed.
-
Enter
subway-streamingin the Name field in the top left of the workspace. -
Click Save & Deploy in the top panel.
-
Check the progress of the pipeline under the Running Pipelines panel of the Overview tab. The data is ready to visualize when the Status is set to Running. Note it may take a few minutes for the pipeline to start running.
Create a View
Now that the data is being streamed to a pipeline containing a Subscriber node, you can create a View with a Data Grid to display the locations of the subway trains that are stopped at stations.
-
Select Visualize on the Overview page, or View from the ribbon menu, as shown below.
-
Click-and-drag a Data Grid, which is the first component on the list, from the icon menu into the central workspace.
-
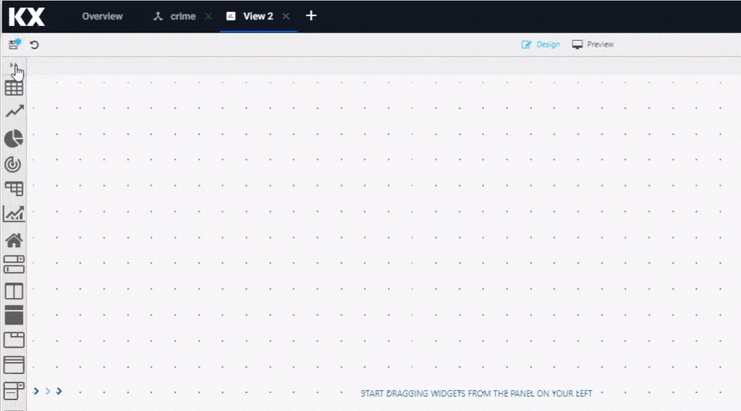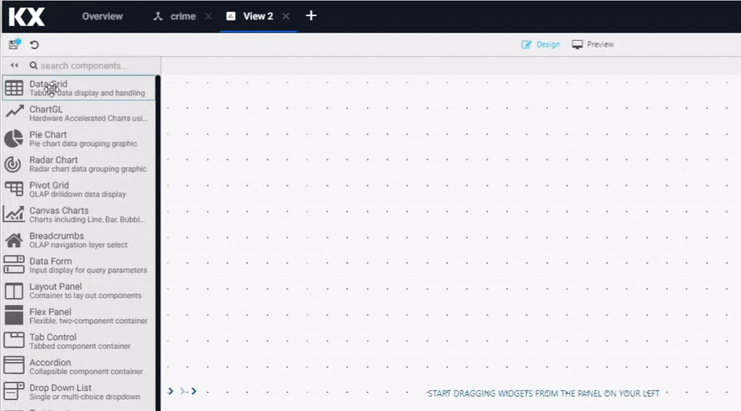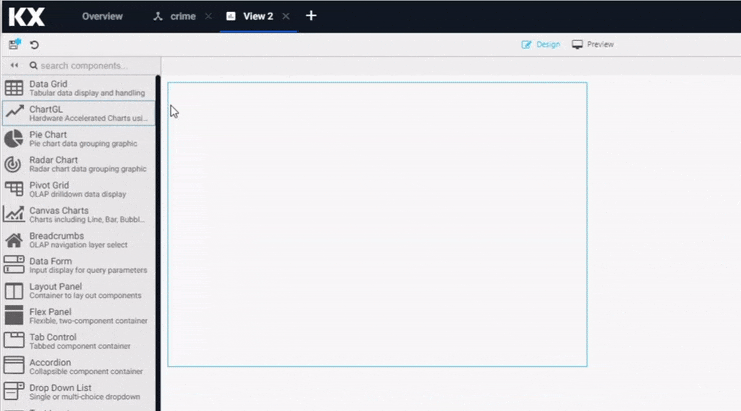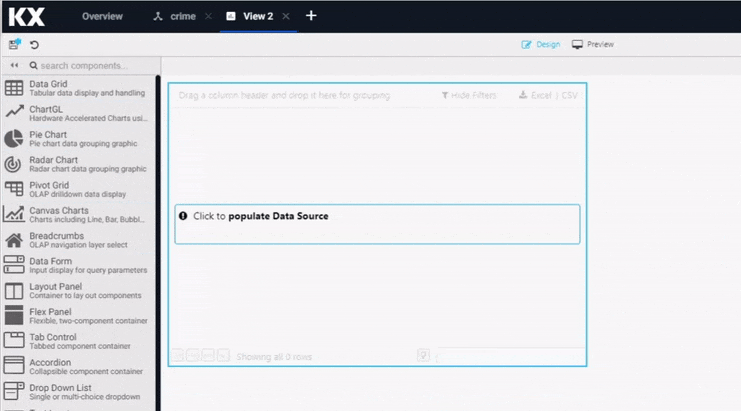
In the Data Grid component, Click to populate Data Source to open the Data editor.
-
Click New to create a new data source and name it
streaming. -
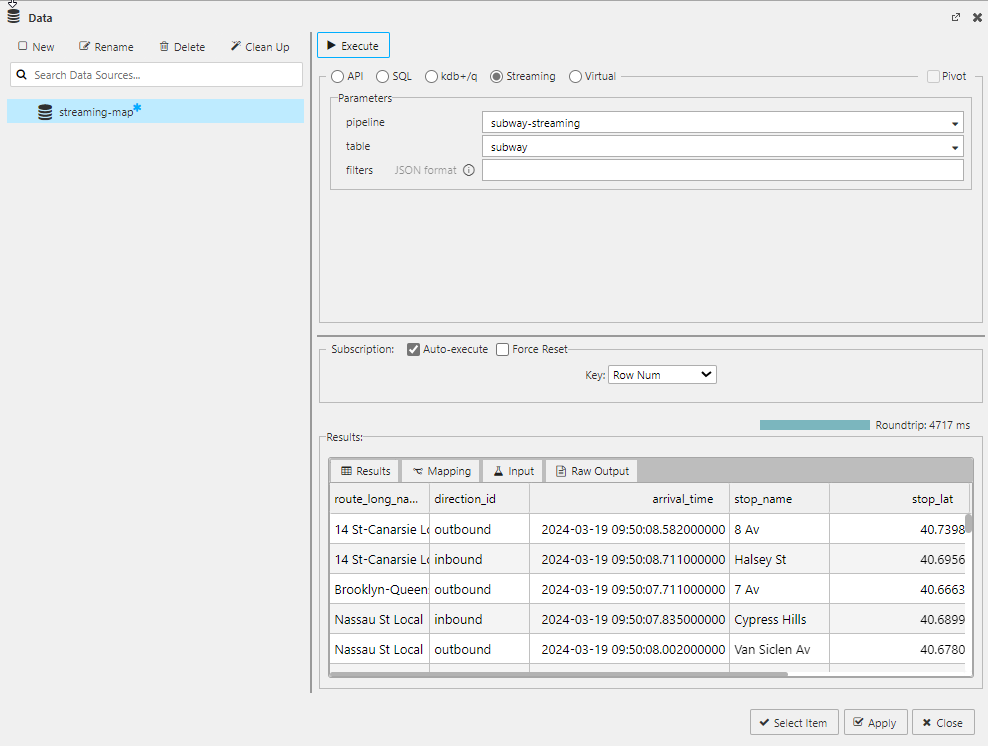
Click on the Streaming radio button and set the following properties:
| value | setting |
|---|---|
| pipeline | This is automatically populated with any running pipelines with a Subscriber node. Select subway-streaming. |
| table | This is automatically populated with tables associated with the pipeline selected. Choose subway. |
| filters | leave empty |
- Click Execute to check the results of the new query. The results are displayed in the Results panel at the bottom of the screen, as shown below. Verify that the streaming position values, with updates visible as data is streamed, are displayed.
-
Click Apply and then Select Item.
-
With the Data Grid selected, set the Sort Column, in the Basics properties, to
route_long_name. -
Save the View by clicking the Save Dashboard icon at the top of the workspace.
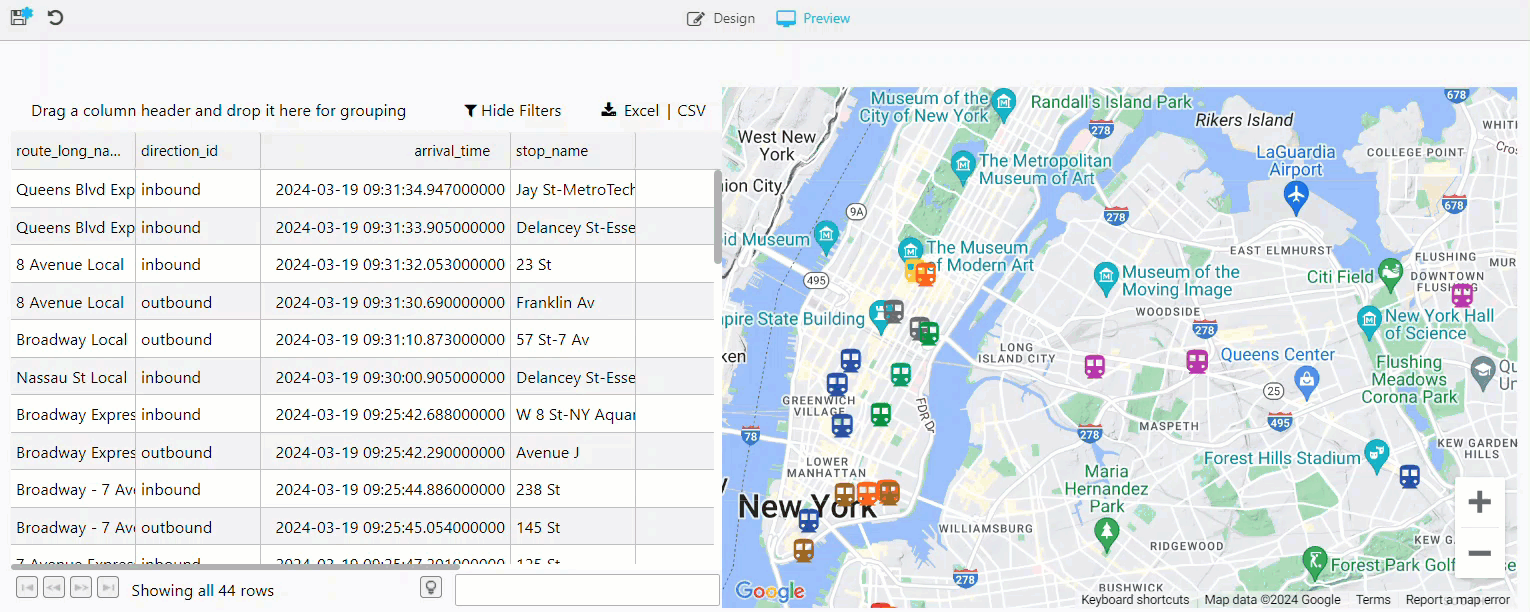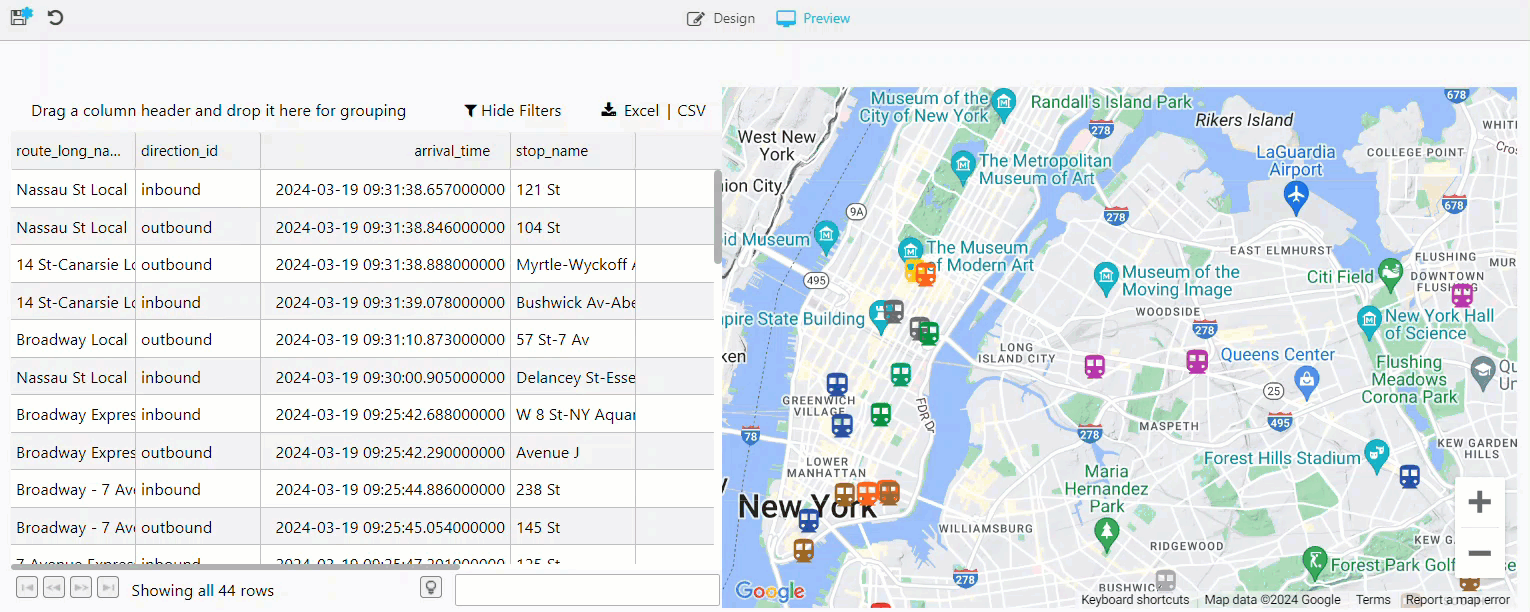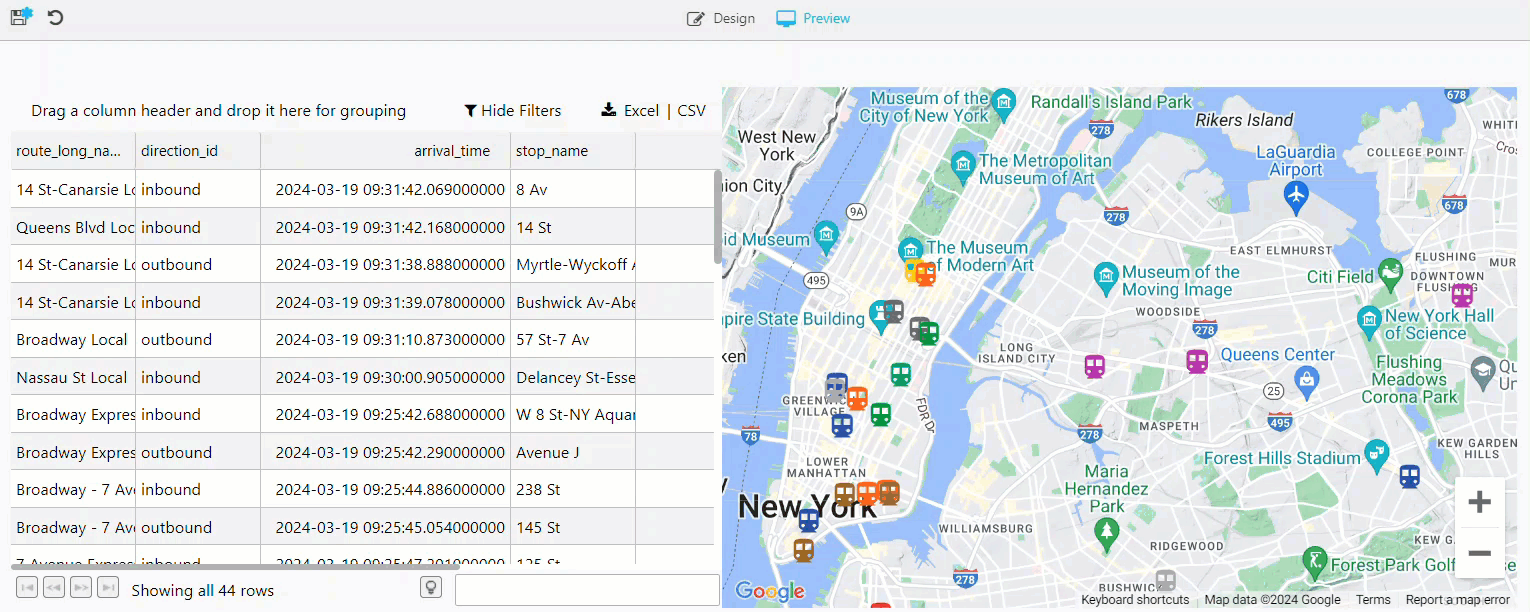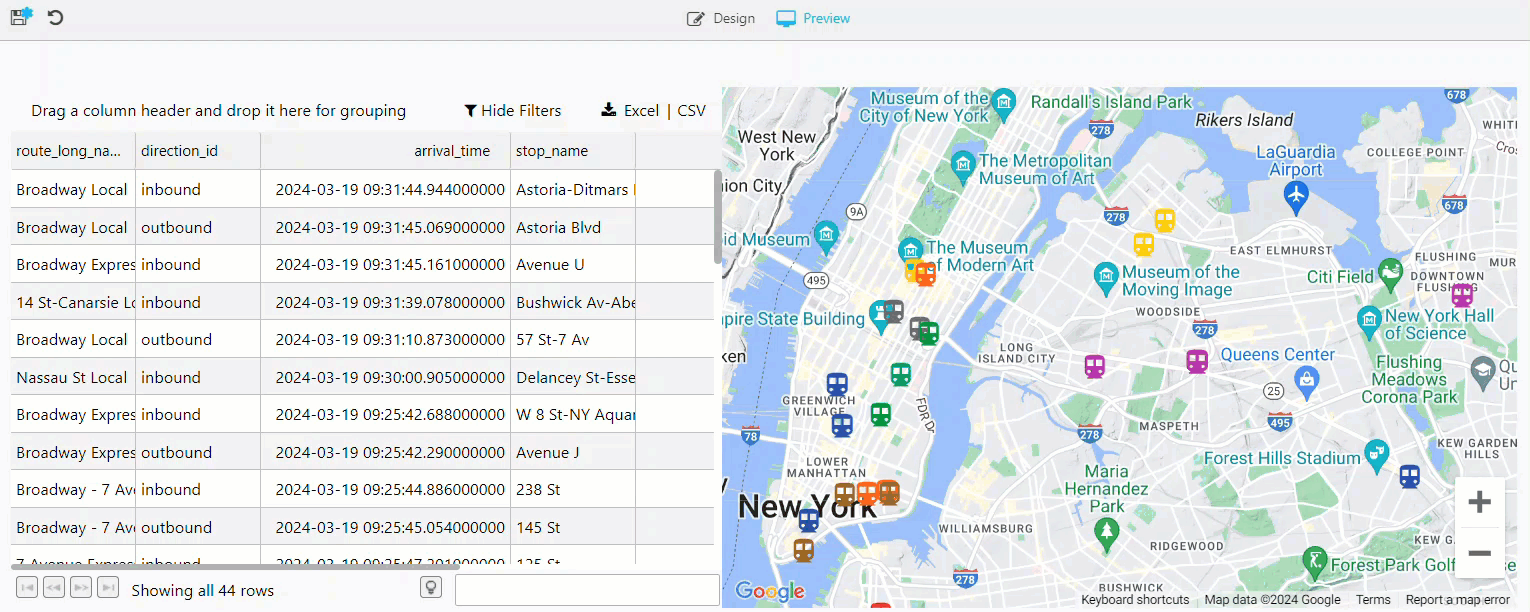
The Data Grid now displays a record per train showing the most recent stop along the NY City subway.
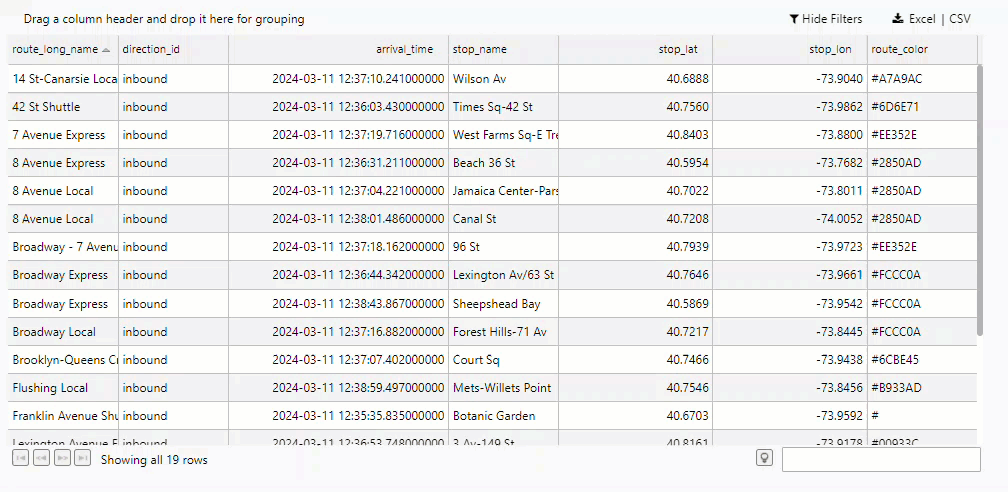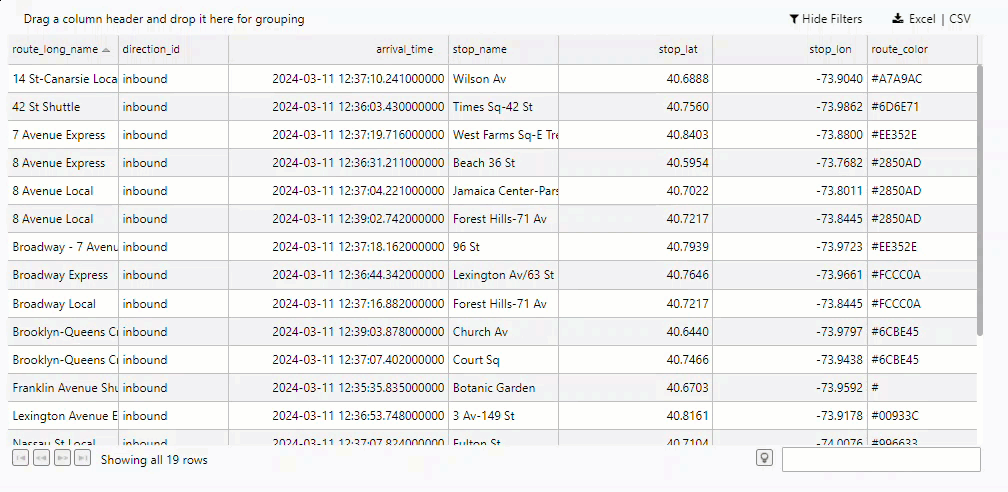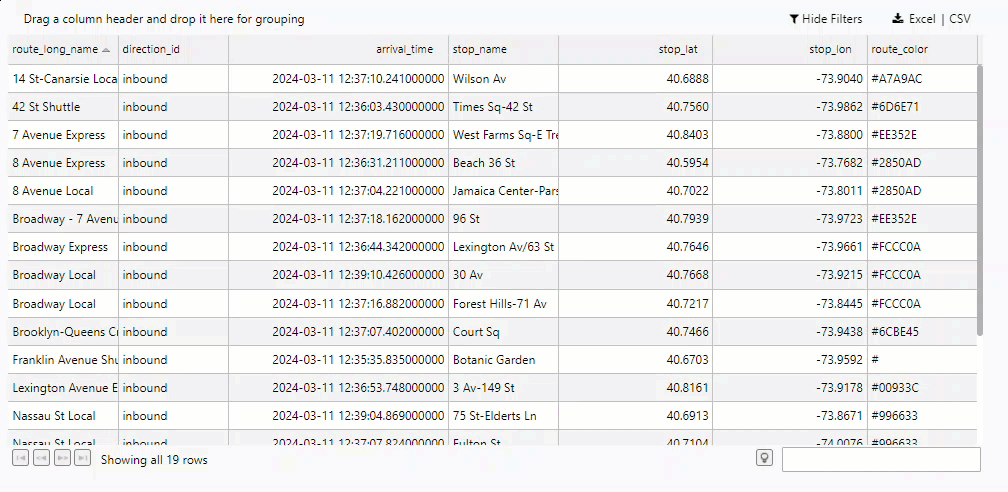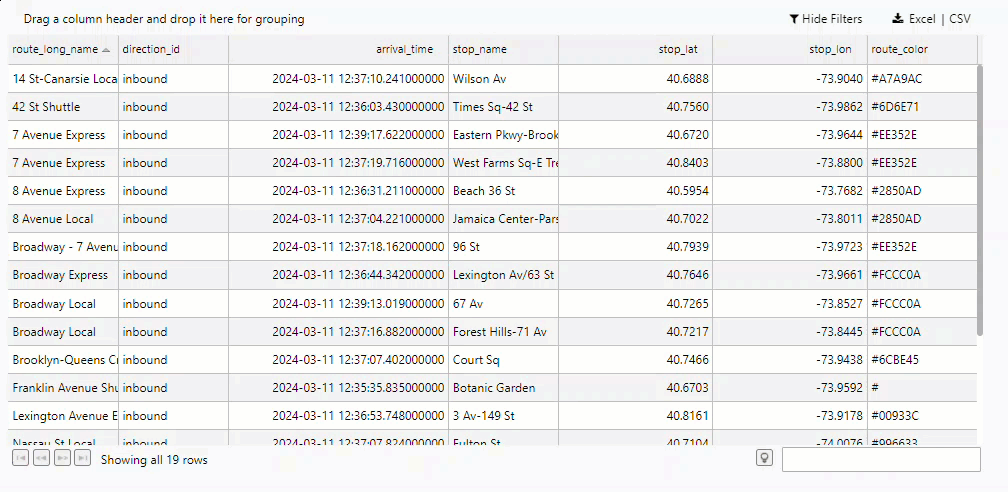
Filtering the Data Grid
Now that you have a View that is being updated with streamed data you can add filters, based on any of the Keyed Columns, to show a subset of the data.
You can only filter on the Keyed Columns, filtering on any other column causes a timeout.
-
With the Data Grid selected in the new View, open the Data Source and choose the
streamingData Source from the list on the left-hand side. -
Type in one of the filters below, which are examples of how filtering can be applied:
filter filter description {"direction_id":"inbound"}All inbound trains {"route_long_name":"6 Avenue Express"}All trains on the 6 Avenue Express route Current filter restrictions
- Filters must be defined using the following JSON format:
{"keyed_column":"value"}. - Only one keyed column can be filtered on.
- Only one value can be applied to the keyed column.
- Filters must be defined using the following JSON format:
-
Click Execute to check that the results, displayed in the Results panel at the bottom of the screen, have applied the filter to the data.
-
Click Apply and then Select Item.
The Grid now only lists records that match the filter being applied. The following example shows the grid being updated with data for all inbound trains only.

Advanced Filtering using View States
If you are familiar with View States you can pair the value in this filter with another component, for example a dropdown, so that you can choose the filter value in the View.
Add a map
If you have a access to an API Key for Google Maps Platform you can add a Map component to your View to display the subway data.
This step is optional. If you want to proceed you must create an API Key for Google Maps Platform as described here.
To add a map to your View:
-
In the design mode for your View, search for the Map component in the list of components, on the left, and drag it into the workspace.
-
Click on the Map component and configure it as follows:
-
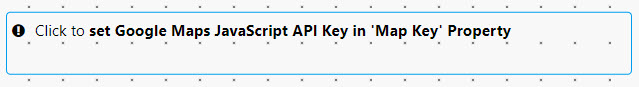
Click "set Google Maps JavaScript API Key in Map Key Property". The Map Key is saved as a view state inside your view.
-
Click New and name the node
mapkey. -
In the Properties section for
mapkey, leave Type set toSymbol. Enter your API Key for Google Maps into the Default and Value properties and click Select Item.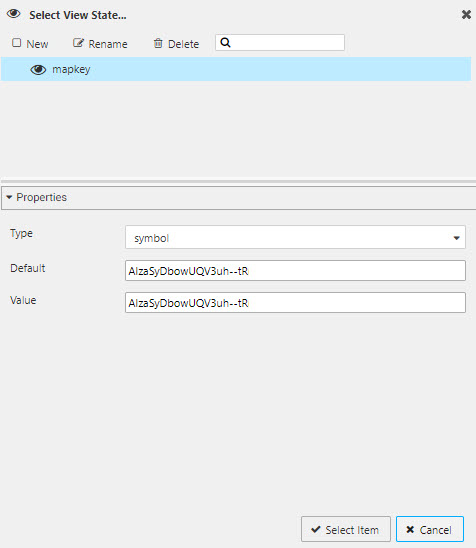
-
Centralize the map on New York by setting the values, in the following table, in the Map properties. These are illustrated in the screenshot below the table.
setting value CenterX 40.75 CenterY -73.98 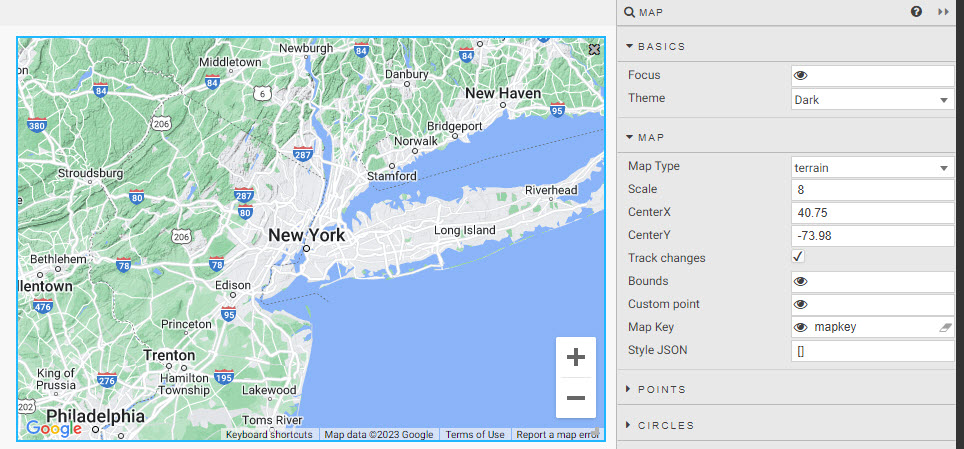
-
-
Define the Data Source from which the component will get data:
-
Click on
Data SourceinPointsproperties. - Create a new data source and name it
streaming-map.
!!!note "If you are want to share the filtering options that you setup for the Data Grid, select the existing streaming data source here."
-
Click on the Streaming radio button and set the following properties:
value | setting --------- | ------- pipeline | subway-streaming table | subway filters | leave empty -
Click Execute to check the results are displayed in the Results panel at the bottom of the screen, as shown below. This displays the streaming position values with updates visible as data is streamed.

-
Click Apply and then Select Item.
-
To ensure the trains are named, positioned and coloured on the map based on the streaming data set the Points properties as follows:
properties value Selected Attr route_long_name Latitude Data stop_lat Longitude Data stop_long Shape train Shape Colour (From DB) route_colour Cluster Unchecked -
Save the View by clicking the Save Dashboard icon at the top of the workspace.
Your View now contains a data grid and a map updating for all inbound and outbound trains, as illustrated below.