Using a package within kdb Insights Enterprise
Once a package that includes Custom APIs and UDFs has been uploaded to kdb Insights Enterprise, there are three components that can utilize them:
The UI does not currently support the creation or modification of Custom APIs and UDFsin a package, these need to be added using the CLI.
Scratchpads
As discussed within the analyzing your data section of the documentation, packages and UDFs can be used within the scratchpad panel of the Query window.
The following examples show you how you can interact with a package test_pkg generated using the Python or q APIs:
import kxi.packages as pakx
import pykx as kx
# List available packages
pakx.packages.list()
# List available UDFs
pakx.udfs.list()
# Load a package and test available variable has been loaded
pakx.packages.load('test_pkg', '1.0.0')
kx.q('.test.variable')
# Retrieve a defined UDF and output it's definition
udf = pakx.udfs.load("custom_map", "test_pkg")
udf
# Generate some test data to use the udf
test_data = kx.q('([]100?1f;100?1f)')
udf(test_data, {'column': 'x1', 'threshold': 0.5})
// List available packages
.kxi.packages.list.all[]
// List available UDFs
.kxi.udfs.list.all[]
// Load a package and test available variable has been loaded
.kxi.packages.load["test_pkg";"1.0.0"]
.test.variable
// Retrieve a defined UDF and output it's definition
udf:.kxi.udfs.load["custom_map";"test_pkg"]
udf
// Generate some test data to use the udf
testData:([]100?1f;100?1f)
udf[testData;`column`threshold!(`x1;0.5)]
Stream Processor
Within the Stream Processor you can utilize your UDFs in the Function node definitions using Python or q.
For more information on retrieval and wrapping of these functions for use with the Stream Processor, refer to Operators for Python and UDFs for q. In both cases, the Stream Processor pipeline being deployed is as follows:
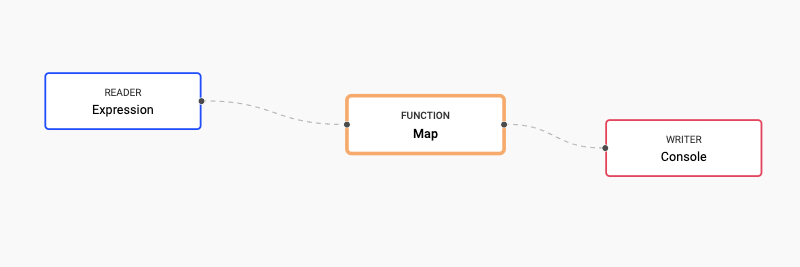
The following steps show the usage of the UDF custom_map stored a test_pkg package.
-
Define an Expression node as follows:
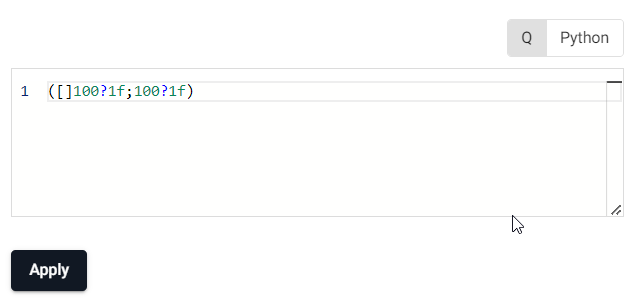
([]100?1f;100?1f) -
Define a Map node to call the
custom_mapstored atest_pkgpackage as follows: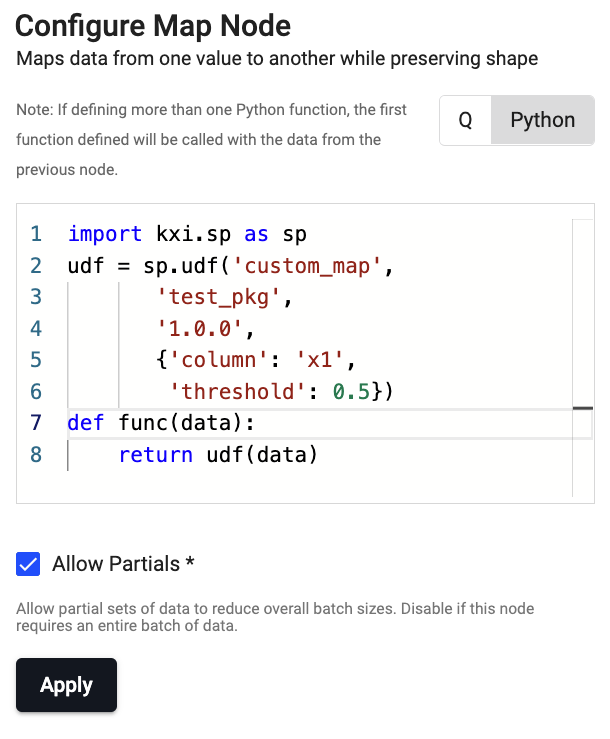
SP Python Node Code
import kxi.sp as sp udf = sp.udf('custom_map', 'test_pkg', '1.0.0', {'column': 'x1', 'threshold': 0.5}) def func(data): return udf(data)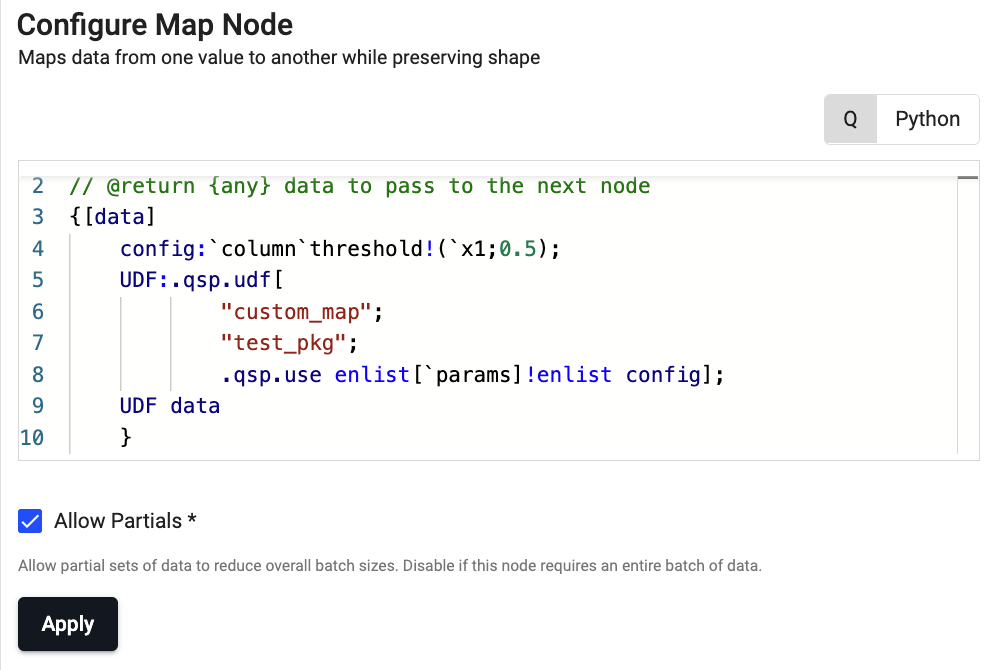
SP q Node Code
{[data] config:`column`threshold!(`x1;0.5); UDF: .qsp.udf[ "custom_map"; "test_pkg"; .qsp.use enlist[`params]!enlist config]; UDF data } -
Define a Console node to display the results.
-
Connect the nodes together.
Using UDFs in an assembly yaml files
The use of assembly yaml files has been deprecated and may be removed from future releases.
You can deploy Stream Processor pipelines to kdb Insights Enterprise through definition within assembly configuration and deployment using the kdb Insights CLI as outlined in Deploying assemblies.
The definition of Stream Processor entries to these files is described fully in the Stream Processor documentation. The examples below show how to define both q and Python pipelines. Each example includes any additional important configuration in addition to the pipeline specification as necessary.
base: py-ml
spec: |-
import pykx as kx
import kxi.sp as sp
import kxi.packages as pakx
pakx.packages.load('test_pkg', '1.0.0')
udf = sp.udf(
'custom_map',
'test_pkg',
'1.0.0',
{'columns': 'x', 'threshold': 0.5})
sp.run(
sp.read.from_expr('([]100?1f;100?1f)') |
sp.map(udf) |
sp.write.to_console()
)
base: q-ml
spec: |-
.kxi.packages.load["test_pkg";"1.0.0"]
udf: .qsp.udf[
"custom_map";
"test_pkg";
.qsp.use `version`params!("1.0.0";`columns`threshold!("x";0.5))
];
.qsp.run .qsp.read.fromExpr["([]100?1f;100?1f)"] .qsp.map[udf] .qsp.write.toConsole[]
A spec must contain the .qsp.run, .qsp.read and .qsp.write commands.
If you were to define a spec that just contains the loading of a file, even if that file itself contains a valid spec, it is invalid.
For example, the spec below is invalid:
base: q-ml
spec: |-
.kxi.packages.load["test_pkg";"1.0.0","mycustomspec.q"]
The spec must explicitly include the .qsp.run, .qsp.read and .qsp.write commands as below:
base: q-ml
spec: |-
.kxi.packages.load["test_pkg";"1.0.0","mycustomspec.q"]
.qsp.run .qsp.read.fromExpr["([]100?1f;100?1f)"] .qsp.write.toConsole[]
Custom APIs in the Database, Aggregator and Resource Coordinator
Custom APIs can be loaded by the Data Access Processes and Aggregator to allow users to call the Custom APIs from outside kdb Insights Enterprise.
Adding a Custom API to enable custom RESTful queries of your package database involves the below steps, which are detailed thoroughly in the quickstart:
- Adding the
database(and optionallyagg&rc) component(s) to the package - Adding the Custom API entrypoint file(s) to the package with the appropriate name (
data-access,aggregator,resource-coordinator) - Registering the function in the entrypoint file as a Custom API
- Pushing & deploying the package to kdb Insights Enterprise
Once added and registered, it is possible to call the new Custom APIs using RESTful calls.
For more information on the definition of custom query APIs and the addition of custom code to the various database components, refer to Custom APIs.
Deploying Custom APIs to Aggregator & Resource Coordinator without including them in the package
This is not recommended, but is possible if you can't add an agg and rc to the package.
This can be done by editing the global agg and rc processes within kubernetes, setting the environment variable KXI_PACKAGES to the package:version of the package containing the desired custom code in each stateful set.