Query configuration
The kdb Insights Database uses Data Access Processes (DAPs) to serve data for queries. DAPs are split into tiers based on the age of the data. Tiers are typically split into a real-time database (RDB), an intra-day database (IDB), and a historical database (HDB). DAPs are configured under a dap key of the elements field within an assembly file. The data of a given tier is maintained by the mount or mounts for that tier. Different scaling configurations are possible depending on how many tiers are provided to a DAP.
Routing
DAPs are accessed using the routing layer. Routing configuration is set at install time across all assemblies.
Deployment
To see a deployment example of data access processes with the other components of a database, see the Docker deployment example.
User interface configuration
This guide discusses configuration using YAML files. If you are using kdb Insights Enterprise, you can configure your system using the kdb Insights user interface
Configuration
Configuration for the Data Access Process is nested under an elements.dap key within an assembly file.
Deployment
To see a deployment example of data access processes with the other components of a database, see the Docker deployment example.
User interface configuration
This guide discusses configuration using YAML files. If you are using kdb Insights Enterprise, you can configure your system using the kdb Insights user interface
| name | type | required | description |
|---|---|---|---|
mountName |
string | No | References the name of the mount this DAP will use to surface data. Either mountName or mountList (but not both) must be provided depending on the desired scaling mode. Providing mountName will use single mount mode. |
mountList |
string[] | No | References a set of mounts this DAP will use to surface data. Either mountList or mountName (but not both) must be provided depending on the desired scaling mode. Providing mountList will use multiple mount mode. |
pctMemThreshold |
float | No | This threshold limits the amount of memory that is used before the DAP triggers a cache flush. This value is a decimal value between 0 and 1. When this value is exceeded, the DAP will enter low memory mode until the next writedown interval completes. |
Scaling configurations
DAPs can be configured in two different modes depending on the anticipated query requirements. DAPs can either be configured to scale independently per data tier, or uniformly across all data tiers.
Scaling Independently
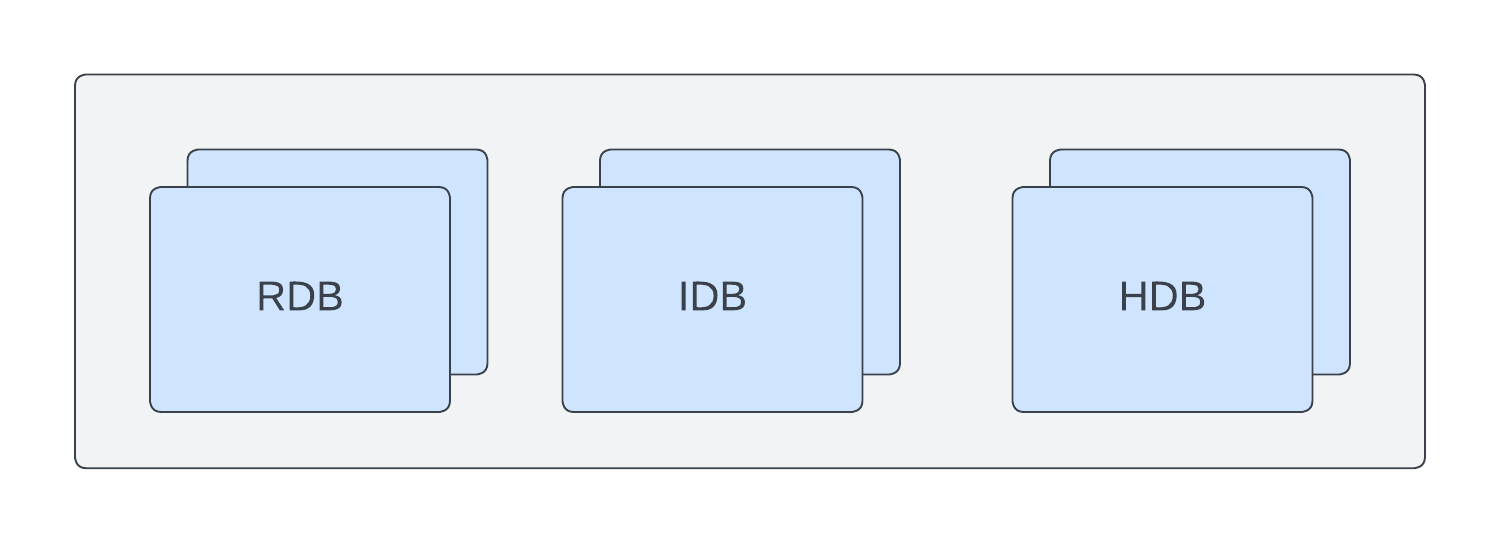
Scaling independently means that you can have more RDBs than IDBs or HDBs, or vice versa. This allows you to tailor your setup to match the anticipated query distribution across the data tiers to maximize query throughput. Scaling independently means that each tier will consume its own set of resources and will run its own container. To use this mode, configure your DAP with the mountName configuration option.
elements:
dap:
instances:
rdb:
mountName: rdb
idb:
mountName: idb
hdb:
mountName: hdb
Scaling Uniformly
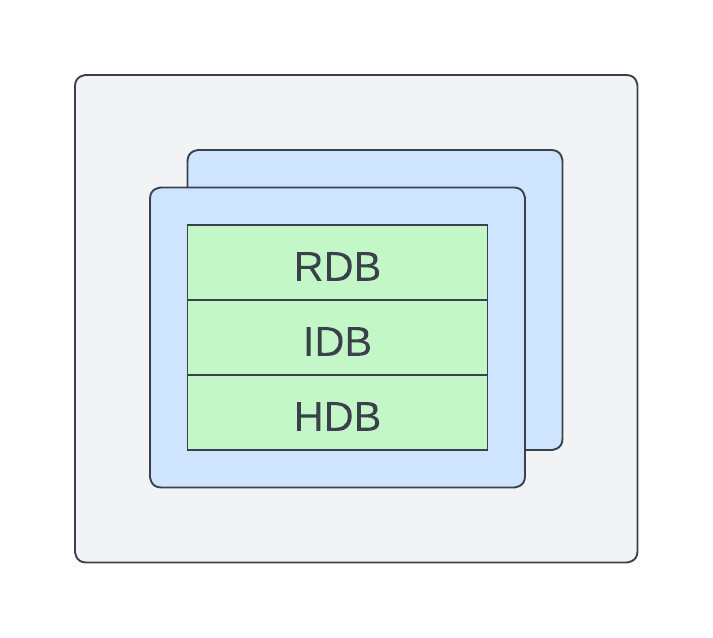
To share container resources, you can scale your DAPs uniformly in a single container. This mode is typically referred to as single DAP mode. In this mode, RDBs, IDBs and HDBs are all within a single container. In this mode, adding another instance adds another copy of all configured tiers. To use this mode, configure your DAP with the mountList configuration option.
elements:
dap:
instances:
db:
mountList: [rdb, idb, hdb]
Environment Variables
Advanced configuration can be supplied to a DAP using environment variables. Environment variables are configured differently depending on the method of deployment. In all cases, the variables are always string values.
In Docker, environment variables are supplied using under an environment key for the target service as a list of key-value pairs.
services:
da:
environment:
- KXI_NAME=da
In Kubernetes, environment variables are supplied as part of a container specification under an env key. Values under the env key are a list of objects with a name and value.
spec:
containers:
- name: kxi-da
image: ${kxi_da}
env:
- name: KXI_NAME
value: "da"
| name | description |
|---|---|
KXI_NAME |
Process name. |
KXI_SC |
Service class for data access (e.g. RDB, IDB, HDB). Must match value in elements.dap.instances of assembly. |
KXI_ASSEMBLY_FILE |
Assembly YAML file. |
KXI_PORT |
Port. |
KXI_CUSTOM_FILE |
File containing custom code to load in DA processes. |
KXI_DAP_SANDBOX |
Whether this DAP is a sandbox (default: false). |
SBX_MAX_ROWS |
Maximum number of rows, per partitioned table, to store in memory. |
KXI_ALLOWED_SBX_APIS |
Comma-delimited list of sandbox APIs to allow in non-sandbox DAPs (e.g. .kxi.sql,.kxi.qsql). |
KXI_DA_RELOAD_STAGGER |
Time in seconds between DAPs of the same class reloading after an EOX (default: 30). |
KXI_DA_USE_REAPER |
Whether to use KX Reaper and object storage cache (default: false). |
KXI_SAPI_HB_FREQ |
Time in milliseconds to run the heartbeat to connected processes (default: 30000). |
KXI_SAPI_HB_TOL |
Number of heartbeat intervals a process can miss before being disconnected (default: 2). |
KXI_GC_FREQ |
Frequency in milliseconds to run garbage collect in a timer (default: 600000, set to 0 to disable). |
KXI_ENABLE_FLUSH |
Set to "true" to enable async flush on messages from DA to Agg (default false). |
KXI_RT_EVENT_FATAL |
If "true", RT badtail and badmsg events are treated as fatal; SM crashes and ingestion stops. If "false" or unspecified, events are logged but ingestion continues. Note that reset events are never treated as fatal. |
KXI_SG_RC_ADDR |
A URL address for an explicit Resource Coordinator for this specific DAP instance to connect to. This must be a fully qualified host name and port. If not specified, the DAP will fallback to Kubernetes label discovery, or kdb Insights Service Discovery. |
KX_OBJSTR_INVENTORY_FILE |
Set to path relative to the root of the bucket to use an inventory file. |
KXI_LATE_DATA |
If "true", DAP will run with late data mode on. Takes precedence over elements.dap.instances.*.lateData setting. |
KXI_MAX_CONN_RETRY |
Number of connection retry attempts to perform before restarting the process. (default: 20). |
In addition, the following environment variables apply to both the sidecar and DAP images.
| name | container | description |
|---|---|---|
KXI_CONFIG_FILE |
sidecar | Discovery configuration file. |
KXI_LOG_FORMAT |
ALL | Log message format. |
KXI_LOG_DEST |
ALL | Log endpoints. |
KXI_LOG_LEVELS |
ALL | Component routing. |
KXI_LOG_CONFIG |
ALL | Alternative logging configuration: replaces KXI_LOG_FORMAT, KXI_LOG_DEST, and KXI_LOG_LEVELS. |
Query size limitations
IPC queries routing through the Service Gateway using the SQL, getData or custom APIs have no limitations on size when using version 6 of the q IPC Protocol.
In the response path, queries are streamed through the Gateway when the response size exceeds KXI_SG_STREAM_THRESHOLD bytes.
For RESTful queries, responses are not streamed to the client, the results will be uncompressed, and limited to 2Gb.