Get Data - SQL Database (Health)
SQL database is a relational database, managed using SQL programming language. A health data set on a PostresSQL database has records of air quality, traffic congestion, car and bike accidents for a day in New York.
A password to access the PostgresSQL database is required before deploying.
No kdb+ knowledge required
No prior experience with q/kdb+ is required to build this pipeline. Replace the PostgreSQL connection details with any other to gain similar results.
Optional: Accessing health data using a local PostgreSQL client install
$ psql "sslmode=disable dbname=postgres user=postgres hostaddr=34.132.151.134"
Password for user postgres: dxrHvgtjHHvsOH7B
psql (14.1, server 13.4)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=> \connect health
psql (14.1, server 13.4)
You are now connected to database "health" as user "postgres".
health=> \dt
List of relations
schema | name | type | owner
-------+----------------------+-------+----------
public | health | table | postgres
(5 rows)
1. Create and deploy a database
A database stores data on kdb Insights Enterprise. Available databases are listed under Databases of the Overview home page. If not available, create a database, insights-demo, to store your data. .
To use a pipeline, your database must be deployed and active.
2. Import Data
Open the import wizard by selecting 2. Import from the Overview page. A pipeline is a connection of nodes to read data from source, transform to a kdb+ compatible format, then write to a kdb Insights Enterprise database.
I want to learn more about the import wizard.
3. Select a Reader

Select PostgreSQL from relational readers.
A reader stores details of data to import. Select PostgreSQL Relational database, and enter the details of the PostgresSQL database; required properties are marked with an *.
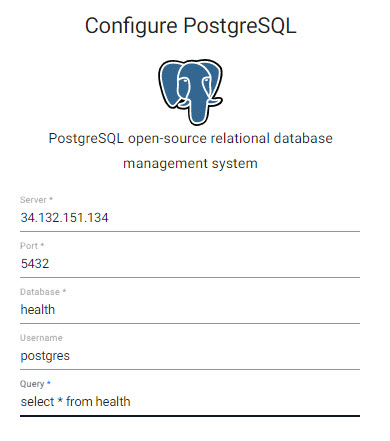
Select PosgresSQL from the relational database import options.
PostgresSQL database hosting health data:
| setting | value |
|---|---|
| Server* | 34.132.151.134 |
| Port* | 5432 |
| Database* | health |
| Username | postgres |
| Query* | select * from health |
Click Next when done.
I want to learn more about reader nodes.
4. Add a Schema
The schema is responsible for converting data to a type compatible with a kdb+ database. Every data table imported requires a schema; and every data table must have a timestamp key to be compatible with kdb's time series columnar database. insights-demo has a predefined schema for the health data set.
| setting | value |
|---|---|
| Apply a Schema | Checked |
| Data Format | Any |
To attach the schema to the data set:
- Click

-
Select
insights-demoschema from the dropdown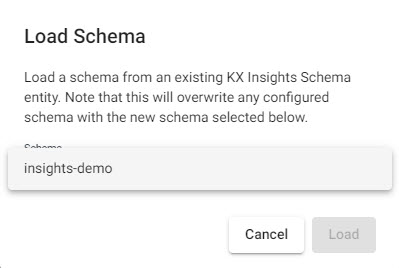
Load schemas from theinsights-demodatabase. -
Select the
healthtable
Select thehealthtable from theinsights-demodatabase.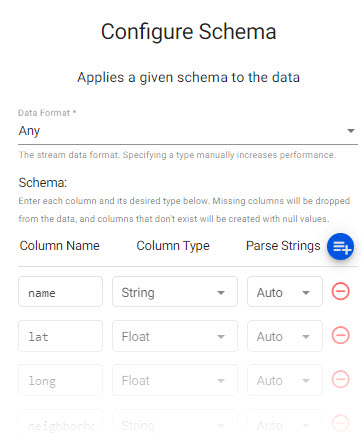
Review thehealthschema; Parse Strings is set asautofor all fields.
Manual entry health schema
If not adding a schema with a table from a database, add the following columns with the  button instead. Column descriptions are optional and not required here:
button instead. Column descriptions are optional and not required here:
| column | type |
|---|---|
| name | string |
| lat | float |
| long | float |
| neighborhood | string |
| airquality | float |
| trafficcongestion | float |
| bikeacccnt | integer |
| caracccnt | integer |
| timestamp | timestamp |
For the name column, set the On-disk Attribute for Ordinal and Temporal Partioning to None. Click the expander (![]() ) icon to update On-Disk attributes.
) icon to update On-Disk attributes.
Parse Strings
Determines the requirement to parse input string data to other datatypes. Generally, parse strings is enabled for all time, timestamp, string fields unless your input is IPC or RT; retain the Auto default if unsure.
Click Next when done.
I want to learn more about transform nodes.
5. Configure the Writer
Write transformed data to kdb Insights Enterprise database.
| setting | value |
|---|---|
| Database | insights-demo |
| Table | health |
| Write Direct to HDB | No |
| Deduplicate Stream | Yes |
Click  to review the pipeline in the pipeline viewer.
to review the pipeline in the pipeline viewer.
A pipeline created by the import wizard, reads data from its source, transforms to a kdb+ compatible format, and writes it to a kdb Insights Enterprise database.
Writer Node
The Writer - kdb Insights Database node is essential for exploring data in a pipeline. The node defines the database to write too that must be active to receive data. Stream data uses its own writer node, Writer - kdb Insights Stream.
I want to learn more about writer nodes.
6. Review the Pipeline
The pipeline is a linked set of nodes derived from each step of the import process.
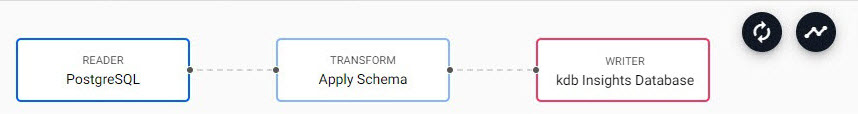
The completed PostgresSQL pipeline.
7. Save the Pipeline
Save the pipeline as health-1.

Save the pipeline as health-1.
Pipeline health-1 is listed under Pipelines in the left-hand menu.
8. Deploy the Pipeline
Deploy a pipeline to access it's data.
Deploy the pipeline.
Deploying a PostgresSQL pipeline requires a password to access the database:
| setting | value |
|---|---|
| password | dxrHvgtjHHvsOH7B |
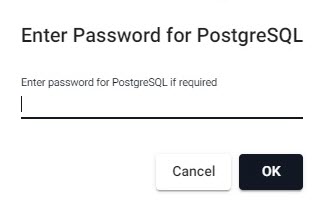
Enter a password to access the PostgresSQL database.
Check the progress of pipeline under Running Pipelines of the Overview panel. The data is ready to query when Status=Running.
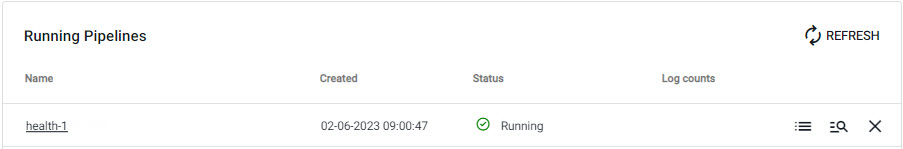
A running health pipeline available for querying.
Database Deployment: If not already active, ensure insights-demo, or the database created with the health schema table, is deployed from Databases in the left-hand menu for it to receive data from the pipeline.
I want to learn more about pipelines
9. Query the Data
Deploy the insights-demo database and health-1 pipeline if not active or running.
Query data on a successful deploy to the database.
10. Visualize the Data
Build a visualization from the data.