KXI Operator
Introduction
The KX Insights operator is a kubernetes workload that is responsible for
creating, reconciling and cleaning up Assembly resources in a KX Insights
installation.
When the KXI Operator is deployed to a cluster, it installs CRDs.
A CRD is a Custom Resource Definition. When installed creates two new resources within the cluster, an Assembly and a AssemblyResources.
Helm
If you're upgrading from a previous version or the CRD is already installed, helm will not update the definition.
kubectl get crd/assemblies.insights.kx.comIt is advised, that the CRD is deleted before or reapplied from source
kubectl delete crd assemblies.insights.kx.com A single operator deployment can be responsible for many AssemblyResources and Assembly CR.
Custom Resource Definition
A CRD creates a new resource within your cluster. Once installed a user can create, modify and delete instance of the new resource like any other Kubernetes resource.
To view existing cluster CRD you can run a kubectl command
kubectl get crdNAME CREATED AT
assemblies.insights.kx.com 2022-01-12T16:50:58Z
assemblyresources.insights.kx.com 2022-01-12T07:29:51Z
capacityrequests.internal.autoscaling.gke.io 2021-10-07T07:43:04Z
capacityrequests.internal.autoscaling.k8s.io 2021-06-15T06:52:16Z
...As with other resource, kubectl can be used to create, view details and delete the CRD
Apply
The apply command can be used to create a new resource within your cluster
kubectl apply -f kxi-operator/crds/insights.kx.com_assemblies.yamlcustomresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/assemblies.insights.kx.com configuredThis will create or amend an existing CRD resource within your cluster.
Describe
The describe can be used to give detailed information on the CRD and spec of the expected CR
kubectl describe crd assemblies.insights.kx.comName: assemblies.insights.kx.com
Namespace:
Labels: <none>
Annotations: controller-gen.kubebuilder.io/version: v0.6.1
API Version: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
Kind: CustomResourceDefinition
...Delete
The delete will remove the CRD as well as any instance of the CR.
kubectl delete crd assemblies.insights.kx.com customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io "assemblies.insights.kx.com" deletedInstallation
Installation of the operator is a pre-requisite of the insights installation.
The CLI will check for an existing installation of the kxi-operator before installing insights. If the kxi-operator is not installed within the cluster, the CLI will install the kxi-operator prior to the install of insights
The Operator makes used of a conversion Webhook which requires that the Operator is installed within its own namespace kxi-operator.
Namespace
As of restriction in Helm the namespace must be set to kxi-operator.
If installed within an alternative namespace webhook conversions will fail
On installation two CRDs will have been added to the cluster
The Assembly CRD
kubectl get crd/assemblies.insights.kx.comThe AssemblyResources CRD
kubectl get crd/assemblyresources.insights.kx.comThe Assembly Resource CR
Once the KXI Operator is successfully deployed, the operator will listen for new
AssemblyResources CR, changes to existing AssemblyResources resources, or their
removal.
The AssemblyResources CR defines defaulting and configuration for a cluster namespace. When the operator attempts to reconcile an Assembly CR applied to a given namespace, the AssemblyResource CR is consulted to find default component images, SP Coordinator and Keycloak endpoints.
Deploying an Assembly Resource
On installation of the base Insights application an instance of the AssemblyResource will have been applied to the control-plane.
It may also be applied using kubectl. Users may update or replace the CR after deployment to update defaulting.
Below is the head of our insights_v1alpha1_assemblyresource.yaml example:
apiVersion: insights.kx.com/v1alpha1
kind: AssemblyResource
metadata:
name: assemblyresource-sample
spec:
defaults:
dap:
image: registry.dl.kx.com/kxi-da:0.9.25
portName: "dap"
port: 5080
seq:
rt:
image: registry.dl.kx.com/kxi-rt-sequencer-raft:0.0.38
....For full documentation of the available fields, see the CRD documentation.
Once deployed, you may view namespace AssemblyResources by running:
kubectl get assemblyresourcesNAME DESCRIPTION AGE
insights Assembly Resource for insights 2d22hCRD singular or short name:
kubectl get assemblyresourcekubectl get asrThe Assembly CR
Once the KXI Operator is successfully deployed, the operator will listen for new
Assembly CR, changes to existing Assembly resources, or their
removal.
Currently the operator deploys and manages the following workloads:
- Multiple instances and flavours of Data Access Processes (DAPs).
- Sequencers - RT processes.
- A Storage Manager deployment.
- SP Pipeline requests (Request made to additional KXI SP Coordinator instance)
The goal of an Assembly is to allow users to deploy configurable data pipelines allowing data to be ingested, processed and persisted. A typical pipeline might look like this.
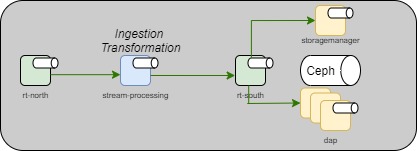
Sample assemblies are available to browse on Nexus along with deployment instructions here. For full documentation of the available fields, see the CRD documentation.
Deploying an Assembly
Assemblies are defined within yaml files and deployed using kubectl.
Below is the head of our basic_assembly.yaml example:
apiVersion: insights.kx.com/v1
kind: Assembly
metadata:
name: basic-assembly
labels:
env: dev
spec:
attach: false
....To deploy this we run the following:
kubectl apply -f config/tests/basic_assembly.yamlassembly.insights.kx.com/basic-assembly createdOnce deployed, you may view all running Assemblies by running:
kubectl get assembliesNAME DESCRIPTION READY STATUS AGE
basic-assembly A KXI Assembly True 93sCRD singular or short name:
kubectl get assemblykubectl get asmTo update your Assembly you may update your yaml file, and repeat the apply.
Changes will be applied to the components and resources dynamically as the KXI Operator will identify what needs to be upgraded.
Assembly Status
The Assembly resource allows for multiple resources to be created.
Each defined element within the Assembly will lead to a StatefulSet to be deployed.
For a quick view of the created resources, a describe may be run on your created Assembly
kubectl describe assembly basic-assembly....
Status:
DAP Status:
Hdb:
Nodes:
basic-assembly-dap-hdb-0
basic-assembly-dap-hdb-1
basic-assembly-dap-hdb-2
Services:
basic-assembly-dap-hdb
Idb:
Nodes:
basic-assembly-dap-idb-0
basic-assembly-dap-idb-1
basic-assembly-dap-idb-2
Services:
basic-assembly-dap-idb
Rdb:
Nodes:
basic-assembly-dap-rdb-0
basic-assembly-dap-rdb-1
basic-assembly-dap-rdb-2
Services:
basic-assembly-dap-rdb
SM Status:
Nodes:
basic-assembly-sm-0
Services:
basic-assembly-sm
SP Status:
Sdtransform:
Nodes:
insights-spctl-sdtransform-q1f4tgjuys-0
insights-spwork-sdtransform-q1f4tgjuys-1-0
Status: INITIALIZING
Seq Status:
North:
Nodes:
rt-basic-assembly-north-0
Services:
rt-basic-assembly-north-0
South:
Nodes:
rt-basic-assembly-south-0
Services:
rt-basic-assembly-south-0The describe will also show you the Assembly configuration, e.g. schema, bus
Delete Assembly resource
Assemblies may removed from the cluster with a simple delete call:
kubectl delete assembly basic-assemblyassembly.insights.kx.com "basic-assembly" deletedWhen a call to delete is made, the resources created directly from the Assembly are removed.
Finalizers
Finalizers are used to make requests to the external KXI SP Coordinator to teardown requested pipelines.
Also note that PVC generated from mount requests, will not be removed.
To remove these the shared label insights.kx.com/app may be used:
kubectl delete pvc -l insights.kx.com/app=basic-assemblypersistentvolumeclaim "basic-assembly-hdb-rook-cephfs" deleted
persistentvolumeclaim "basic-assembly-idb-rook-cephfs" deleted
...