IPC interface example
This example provides a quickstart for interfacing with external q processes using KDB-X Python (pykx).
This example should work whether or not a k4.lic file is present. The purpose is to show the flexibility of this interface for users who had previously used KDB-X Python (pykx) or are familiar with qPython.
To follow along, feel free to download this zip archive that contains a copy of the Python script and this writeup.
Quickstart
This example shows a basic tickerplant configured as follows:
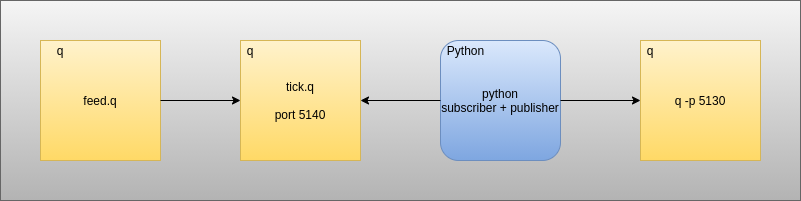
Here we have:
- A q data feed publishing trade messages to a tick process.
- A q process running a modified
tick.q. - A Python process subscribing to the tick process, running a Python analytic on the trade data and pushing the results to another process.
- A q process to which the results of the Python analytic can be pushed.
For more information about the differences between the licensed and unlicensed versions of this example consult readwrite.py for a breakdown of the steps taken in the presence/absence of a licensed shared object.
Start the required q processes
// run tick.q
$ q tick/tick.q sym ./log/
q)
// run the mock feed
$ q tick/feed.q
q)
// Start the q process to receive data from `pykx`
$ q -p 5130
q)Start the pykx subscriber/publisher
// When running with a valid k4.lic in $QHOME
$ python readwrite.py
Running example in presence of licensed q
// When running in the absence of a valid k4.lic in $QHOME
'2021.04.02T11:32:41.006 license error: k4.lic
Running example in absence of licensed qOutcome
On invocation of the above, the process running on 5130 should begin to receive summaries of the average size/price of the individual tick symbols being published. The licensed and unlicensed versions are not the same in this regard.
- The licensed version will return the average over the entire trade table that it is subscribed to
- The unlicensed version will display the the average over the most recent batch of data received